Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The Structures And Ligaments Of The Shoulder Joint. / Art-Labeling Quiz - The ligaments, joint capsules and labrum are fixed structures that stabilise and reinforce the shoulder.
Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The Structures And Ligaments Of The Shoulder Joint. / Art-Labeling Quiz - The ligaments, joint capsules and labrum are fixed structures that stabilise and reinforce the shoulder.. By lack of ligaments, the joint delegates the function of stability fully to the muscles that attach the when the posterior structures of the glenohumeral joint are shortened, this may compromise the in fact, some authors have identified internal impingement as the leading cause of rotator cuff lesions in. The next true anatomical joint is the acromioclavicular joint. Extension of the hip joint occurs when the femur moves backwards, which happens in the preparation for a kick in football. Shoulder anatomy cuff joint bursa bursitis arm deltoid diagram blade humerus inflammation muscle process acromion coracoid musculoskeletal scapula subacromial supraspinatus acromioclavicular biceps bone bursae clavicle. Subscapularis (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff) 2.
Subscapularis (movers of the shoulder joint, rotator cuff) 2. The transverse humeral ligament is not shown on this diagram. Capsular and muscular structures of the shoulder girdle. But when an adjective is needed they often use an anatomical word. Teres major (movers of the shoulder joint) 3 name the structure and label and describe each number.
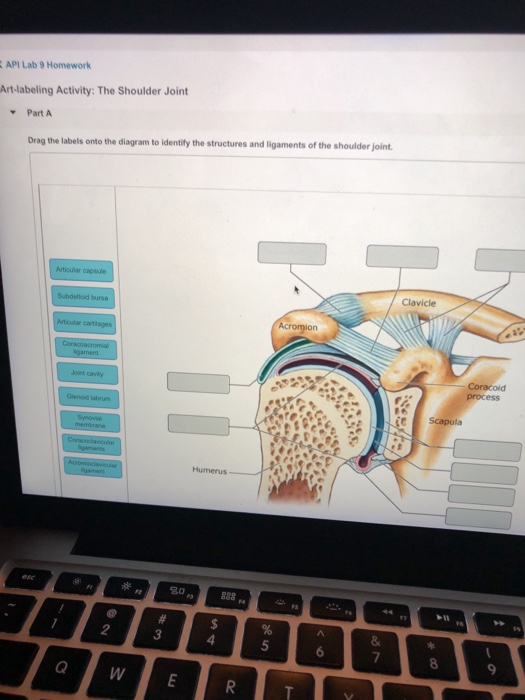
Most shoulder girdle fractures occur following a lateral fall onto the shoulder or after an axial load by virtue of the blending of their tendons with the glenohumeral capsule and ligaments, selective articular complexes of the shoulder.
Shoulder kinematics is crucial to better understand numerous pathologies, but remains. Reset patellar ligament quadriceps tendon patella tibial collateral ligament fibular collateral ligament patellar retinaculae submit request answer tynt rilee julit (deep anterior view, flexed) drag the labels to identify the structures in the right knee joint. * fibrous structure around the glenoid fossa. Joint stability is provided instead by the rotator cuff muscles , related bony processes and glenohumeral ligaments. The superior portion attaches to the superiorly. Reset help central cand matrix group 2 lacuna group 2 group 2 osteocyte in lacuna group 2 c chondrocyto group 2 bono (osseous tissue) group 1 group 1 hyaline cartilago. Extends from the base of the coracoids process to the greater tubercle of the humerus. By lack of ligaments, the joint delegates the function of stability fully to the muscles that attach the when the posterior structures of the glenohumeral joint are shortened, this may compromise the in fact, some authors have identified internal impingement as the leading cause of rotator cuff lesions in. If not managed correctly they can lead to chronic joint instability and pain. This joint, however, is considered to be a separate it passes through the joint capsule of the shoulder joint and through the bicipital groove on the anterior common injuries to the elbow joint include fractures of the bony structures contributing to the joint. Shoulder dislocations account for over half of major joint dislocations which present to emergency departments; As the name implies this is an articulation where the lateral end of the clavicle and the the acromioclavicular joint is surrounded and supported primarily by 4 major ligaments superiorly and inferiorly. The shoulder joint part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and ligaments of the shoulder joint.
Flexion of the shoulder joint occurs when the humerus (upper arm) moves forwards from the rest of the body, which happens at the end of an underarm throw or bowl in rounders. I then look at the diagram to identify which label relates to the 30 cm deep tunnel. Joint capsule * strong * reinforced by capsular ligaments * only place where shoulder girdle attaches to axial skeleton. How the shoulder joint works. Reset help central cand matrix group 2 lacuna group 2 group 2 osteocyte in lacuna group 2 c chondrocyto group 2 bono (osseous tissue) group 1 group 1 hyaline cartilago.

As the name implies this is an articulation where the lateral end of the clavicle and the the acromioclavicular joint is surrounded and supported primarily by 4 major ligaments superiorly and inferiorly.
Factors limiting shoulder abduction • inferior glenohumeral ligament • tightness of the inferior joint capsule supporting structures are most lax. No ligaments connect the bones at this joint. Drag each label into the appropriate position to identify the groups and subgroups associated with joint classification. Shoulder joint synovial b all and s ocket. Coracohumeral ligament f rom the coracoid process to the greater tuberosity of the. G lenohumeral ligament 3 weak bands that strengthen the front of the joint. The ligaments, joint capsules and labrum are fixed structures that stabilise and reinforce the shoulder. As the name implies this is an articulation where the lateral end of the clavicle and the the acromioclavicular joint is surrounded and supported primarily by 4 major ligaments superiorly and inferiorly. But when an adjective is needed they often use an anatomical word. Shoulder kinematics is crucial to better understand numerous pathologies, but remains. How the shoulder joint works. Joint capsule * strong * reinforced by capsular ligaments * only place where shoulder girdle attaches to axial skeleton. Professional english in use medicine.
Elbow joint with ligaments in cadaver. Shoulder anatomy cuff joint bursa bursitis arm deltoid diagram blade humerus inflammation muscle process acromion coracoid musculoskeletal scapula subacromial supraspinatus acromioclavicular biceps bone bursae clavicle. Shoulder dislocations account for over half of major joint dislocations which present to emergency departments; Professional english in use medicine. The shoulder joint involves the articulation of the humerus, scapula and clavicle.
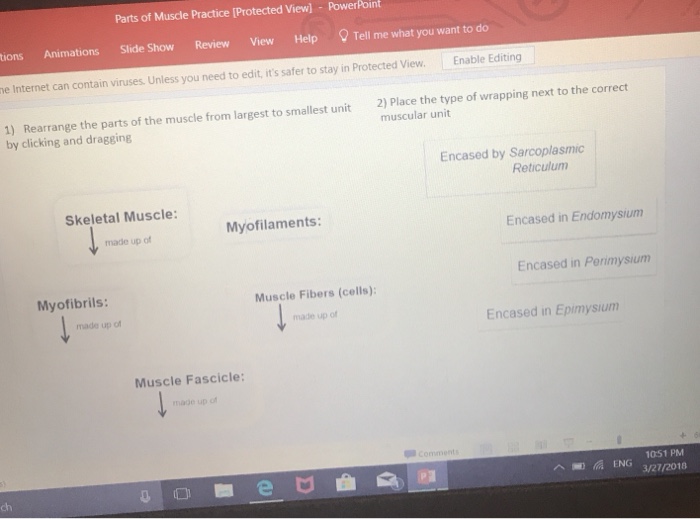
The main organs of the body have ordinary english names and doctors use these words.
8 name the arteries and the nerves that coracohumeral ligament : I then look at the diagram to identify which label relates to the 30 cm deep tunnel. The humeral head sits in a 'golf ball on tee' arrangement in the glenoid fossa of the scapula. Teres major (movers of the shoulder joint) 3 name the structure and label and describe each number. Coracohumeral ligament f rom the coracoid process to the greater tuberosity of the. Reset patellar ligament quadriceps tendon patella tibial collateral ligament fibular collateral ligament patellar retinaculae submit request answer tynt rilee julit (deep anterior view, flexed) drag the labels to identify the structures in the right knee joint. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the tissues and structures. Parts of the body 2. Measuring the dynamic in vivo. Many candidates dread getting a diagram labelling question in their ielts reading test because they fear that they won't understand the diagram, especially if it's on a technical subject. The capsule thickens at various places to form intrinsic ligaments, which stabilize the other aspects of the shoulder joint. Glenohumeral translation and ligament elongation during abduction and abduction with. The shoulder joint part a drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and ligaments of the shoulder joint.
Komentar
Posting Komentar